4T1-mNIS-Neo/iRFP-Puro
- Frozen / Standard (CL108-STAN) $ 2,100
Species: Mouse
Cell type: Mammary carcinoma
Transgenes: Murine sodium iodide symporter (mNIS) with neomycin resistance (Neo) for selection with G418 and near-infrared fluorescent protein (iRFP; excitation/emission: 690/713nm) with puromycin resistance (Puro) for selection with puromycin
Media: RPMI, 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep, 0.1 mg/mL G418, 2 μg/mL puromycin
Description:
4T1-mNIS-Neo/iRFP-Puro is a polyclonal population of the murine mammary carcinoma cell line 4T1 (ATCC® CRL-2539™) transduced with 1) LV-mNIS-P2A-Neo (LV025) encoding the murine sodium iodide symporter (mNIS) cDNA under the spleen focus-forming virus (SFFV) promoter linked to the neomycin resistance gene (Neo) via a P2A sequence and 2) LV-iRFP-P2A-Puro (LV032) encoding the near-infrared fluorescent protein (iRFP) cDNA under the spleen focus-forming virus (SFFV) promoter linked to the puromycin resistance gene (Puro) via a P2A cleavage peptide
The lentiviral vectors used are self-inactivating (SIN) vectors in which the viral enhancer and promoter has been deleted. Transcription inactivation of the LTR in the SIN provirus increases biosafety by preventing mobilization by replication competent viruses and enables regulated expression of the genes from the internal promoters without cis-acting effects of the LTR (Miyoshi et al., J Virol. 1998).
Mycoplasma Testing:
The 4T1-mNIS-Neo/iRFP-Puro cell line has been tested for mycoplasma contamination and is certified mycoplasma free.
Cell Line Authentication:
The parental 4T1 cell line was authenticated and certified free of interspecies cross-contamination by short tandem repeat (STR) profiling with 27 STR loci.
Recommended uses:
In vitro: This is a high mNIS/iRFP expressing cell line suitable for use as a positive control cell line in iodine uptake and fluorescence assays to verify NIS or iRFP expression respectively in your lentiviral transduced cells.
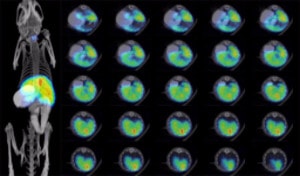
In vivo: 4T1 cells form tumors post implantation into mice. The in vivo growth of these tumors can be monitored using noninvasive, high-resolution 3D PET/SPECT imaging or noninvasive optical imaging. Please ensure that your optical imaging systems have the correct excitation and emission filters for detection of iRFP.
Morphology: Low- and high-density cell morphology (200x)

NIS Function Assay (Iodine Uptake): Cells were incubated with 125I for 1h in the presence or absence of KClO4, an inhibitor of NIS mediated iodine uptake. Radioiodine concentrated within the cells was measured with a gamma counter.

Flow Cytometry for iRFP: 4T1-mNIS-Neo/iRFP-Puro (red) or isotype control (4T1-Fluc-Neo; grey) cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde and analyzed by flow cytometry (20,000 events).