Species-Specific Sodium Iodide Symporters
pLV-CAG-mouseNIS-P2A-Neo starting at $ 1,500
pLV-PGK-mouseNIS-P2A-Neo starting at $ 1,500
pLV-SFFV-mouseNIS starting at $ 1,500
pLV-SFFV-mouseNIS-P2A-Neo starting at $ 1,500
pLV-SFFV-mouseNIS-PGK-Puro starting at $ 1,500
pLV-TBG-mouseNIS starting at $ 1,500
pLV-Ub-mouseNIS-P2A-Neo starting at $ 1,500
pLV-SFFV-ratNIS starting at $ 1,500
pLV-SFFV-ratNIS-Puro starting at $ 1,500
pLV-SFFV-dogNIS starting at $ 1,500
pLV-SFFV-dogNIS-PGK-Puro starting at $ 1,500
pLV-EF1a-rhesusNIS-PGK-Puro starting at $ 1,500
pLV-SFFV-rhesusNIS starting at $ 1,500
pLV-SFFV-rhesusNIS-PGK-Puro starting at $ 1,500

Description
The sodium iodide symporter (NIS) is a membrane protein that drives uptake of iodine into cells. Mammals express NIS endogenously in the thyroid, salivary glands, gastric mucosa, and mammary glands. And other cell types and viruses can be engineered to express recombinant NIS.
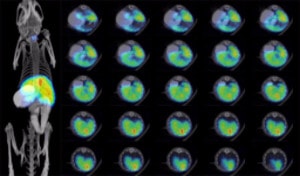
NIS concentrates radioactive iodine as well as several other radiotracers, so it can be used to noninvasively track cells in vivo through nuclear imaging. NIS imaging has several key advantages: it produces high-resolution 3D images that are fully quantitative, it is translational from small to large animals as well as humans, and it can be used for longitudinal imaging studies as the species-specific NIS proteins are non-immunogenic.
How to use NIS for imaging
Reagents: NIS concentrates a number of different radiotracers, several of which are clinically approved.

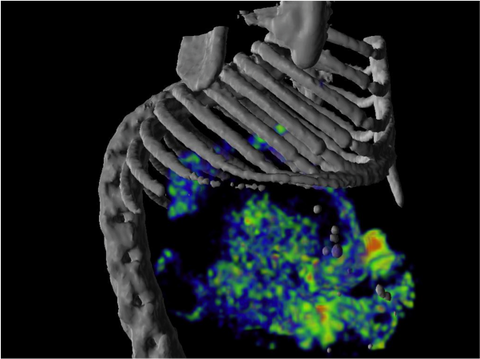
Equipment: SPECT or PET machines can be used to detect radiotracer signal and biodistribution of NIS-expressing cells or virus. Combining SPECT or PET with computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance (MR) imaging gives the most informative results, as images can be co-registered to give anatomical localization of the radiotracer signal.
Additional considerations: Depending on the location of the target organs for imaging, administration of undiluted barium sulfate prior to imaging can be used to block endogenous NIS signal in the stomach.
Workflow:

When to use NIS
NIS is well suited for longitudinal, noninvasive imaging studies in regenerative medicine, gene therapy, oncology, and oncolytic virotherapy, where it can be used to track the biodistribution of cell/virus therapies or the destruction of tumors. NIS can be used for small or large animal imaging and is translatable to the clinic. The heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, orthopedics (joints and bone), and immune cells are all suitable organs for NIS imaging.
Radiotracers used for NIS imaging are actively pumped out of the brain and CNS. Therefore, unless the blood-brain barrier is permeated, NIS is not recommended for brain or CNS imaging. NIS imaging of organs near the stomach may be obscured by endogenous NIS signal from the stomach, which can be blocked with barium sulfate (see Additional considerations, above).